Projections¶
Section author: Luke Frisken <l.frisken@gmail.com>
Introduction¶
Projection classes derived from the Projection class are
used to represent a type of
map projection.
These are important to this project because projections allow the 3d spherical
coordinates to be transformed into flat representation which is easier to work
on.
Different types of projections have different properties making them more or less suitable depending on the application. For our case, it is important that the projection be as close to Euclidean space as possible in the area it is being used. This will allow us to assume such, and simplify our calculations with minimal effect on the accuracy. Performance, and ease of implementation are also factors.
These projections must be capable of transforming a
GeographicCoordinate or SphericalVelocity
into a vector position within its own coordinate system. This is achieved
through the implementation of the methods:
Positions in the projection’s coordinate system are transformed back into
GeographicCoordinate or SphericalVelocity through the
implementation of the methods:
Gnomonic Projection¶
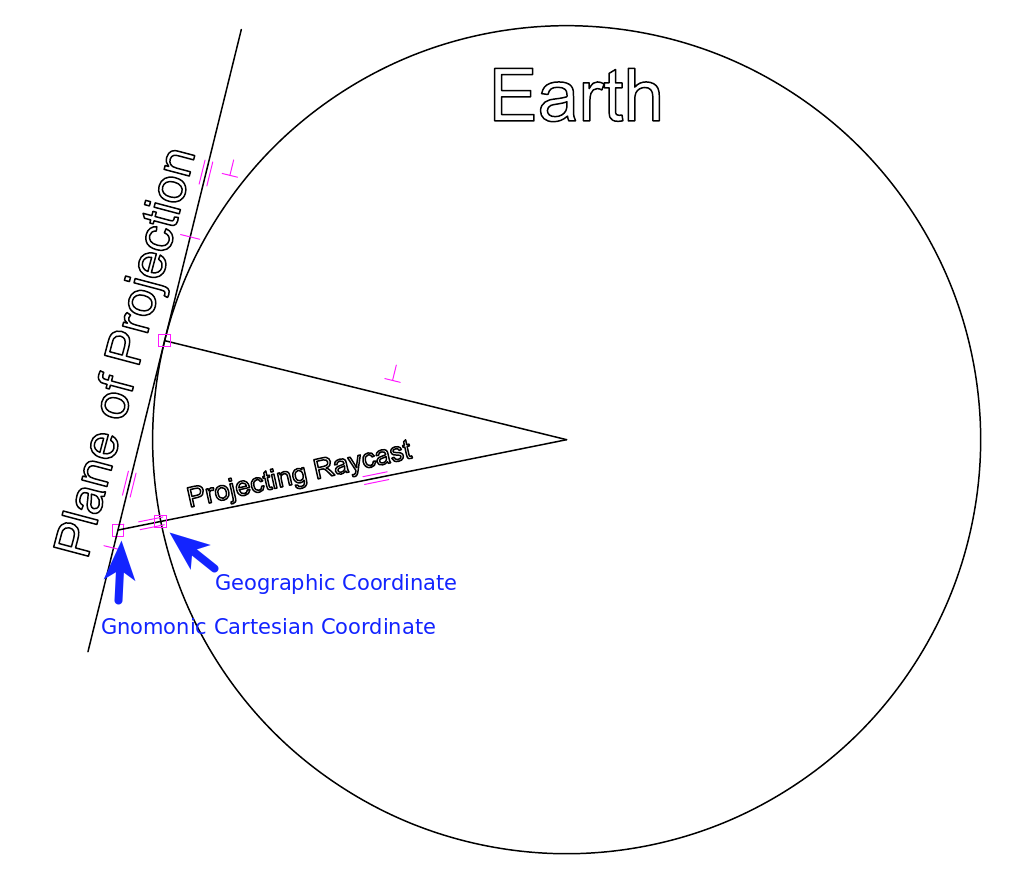
Gnomonic Projection
Gnomonic projection is formed by projecting points on the sphere of the earth
onto a plane, which is located/touching the earth at a certain point known as
the Reference Position within this project. By convention in this project,
this plane has its own coordinate system, with the y axis aligned to the north
direction. The points are projected using a ray which originates from the center
of the earth.
Ensuring that the Reference Position is as close as possible to the points
which are to be projected and worked upon in the projection enables the
simplifying assumption that this is Euclidean space to have minimal impact on
the accuracy of the calculations.
Gnomonic projection capabilities are implmented twice within this project.
The first (and most important) is in the GnomonicProjection class.
The second place is in the display.DisplayApplication, which uses Gnomonic
projection to display the map in OpenGL by placing the camera at the center
of the planet, and rendering the planet and elements on the map in cartesian
space. As OpenGL transforms the elements on the map into 2d screen space,
this is implicitely undergoing a Gnomonic projection.
Stereographic Projection¶
The stereographic projection has yet to be implemented within the project. Many commercial displays use this projection but the implmementation is slightly more complicated, an it is not yet certain whether it will be of any significant benefit.